GraphQL API
Access the commercetools platform via GraphQL API.
The GraphQL API provides queries and mutations to the resources stored on the commercetools platform with the same API Clients that are used for the REST API. This page documents how a valid API request needs to be formulated, how the Scopes are applied, how the query complexity can be determined and how Reference Expansion can be achieved. Furthermore, this page explains how custom fields and attributes can be queried and modified, but it does not document which standard types and fields the API provides. Those information can be retrieved from the GraphQL schema that can be obtained via introspection or via the Documentation Explorer in the GraphQL console. Documented here explicitly are types and fields that are currently in beta.
Application of scopes
The access to resources is granted by the same scopes that are used on the REST API endpoints. We do not document them here in detail, but we give some guideline on how to find the scope best suitable for a use case in general:
| Use case | GraphQL service | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| query for a particular resource | Query.{resourceType} | view_{resourceType}s |
| query for resources of a certain type | Query.{resourceType}s | view_{resourceType}s |
| create a resource of a certain type | Mutation.create{resourceType} | manage_{resourceType}s |
| update a particular resource | Mutation.update{resourceType} | manage_{resourceType}s |
| delete a particular resource | Mutation.delete{resourceType} | manage_{resourceType}s |
For example, the manage_products scope is required for updating a Product with the Mutation.updateProduct service, the view_products scope would not be sufficient for this.
The view_published_products scope can be used by the Query.products service to retrieve data in masterData.current, but not in masterData.staged. The same applies for the Query.productProjectionSearch service that only returns data with this scope when the staged parameter is set to false in such queries.
Query GraphQL
You can access the GraphQL endpoint with following URL:
https://api.{region}.commercetools.com/{projectKey}/graphql
The endpoint accepts HTTP POST requests with following fields in a JSON body:
query- String - GraphQL query as a stringvariables- Object - Optional - containing JSON object that defines variables for your queryoperationName- String - Optional - the name of the operation, in case you defined several of them in the query
Find below an example for a query for id and version of a Product with sku equal to SKU-123 to be executed as cURL command:
$ curl -X POST https://api.{region}.commercetools.com/my-shop/graphql \-H "Content-Type:application/json" \-H "Authorization:Bearer ..." \-d '{"query": "query ($sku: String!) {product(sku: $sku) {id version}}", "variables": {"sku": "SKU-123"}}'
Product attributes and custom fields
Product attributes and custom fields are project-specific dynamic fields that can be accessed using raw GraphQL fields. Raw GraphQL fields provide the values as raw JSON that you have to parse yourself. Queries for such fields ensure consistency and good performance.
Raw product attributes
Pseudo-example for using raw product attributes:
fragment variantFields on ProductVariant {skuattributesRaw {namevalue}}
Raw custom fields
Pseudo-example for using raw custom fields:
fragment customFields on ProducePrice {custom {customFieldsRaw {namevalue}}}
Existence of query results BETA
For use cases in which you only want to check whether at least one result exists that matches your query, we recommend using the Boolean exists field in your query. This way, the platform can optimize the query towards short response time.
query {products(where: "productType(id="some-uuid")") {exists}}
The API returns true in case there is at least one result matching the query condition, but the field value is false in case no matching result could be found.
{"data": {"products": {"exists": true}}}
Reference Expansion
The GraphQL API supports Reference Expansion, just like the HTTP API.
By convention, the GraphQL API offers two fields for each expandable reference:
<fieldName>Ref- Fetches the Reference to the resource only (lower query complexity).<fieldName>- Fetches the expanded resource that is referenced (higher query complexity).
Returnsnullif the referenced resource is not found.
Expanding a reference in the GraphQL API impacts the performance of the request, and adds to the complexity score. If you don't need the expanded reference for your use case, you should use the <fieldName>Ref to get better performance on your query.
For an example, if you want to obtain the number of child categories for a specific category, as well as identifiers for its ancestors, the following query would work:
{category(id: "some-uuid") {children {id}ancestors {id}}}
The total number of child categories will be the size of children array, and the ancestors identifiers are also available from the ancestors.
However, the complexity of the example above can be reduced. If you only need the number of child categories, the childCount field is the way to go. Also, in case you only need the identifiers for the ancestors, it's better to use the ancestorsRef field. This is how the less complex query looks like:
{category(id: "some-uuid") {childCountancestorsRef {id}}}
Query complexity
You can fetch a lot of useful information in a single HTTP request using GraphQL. This is really helpful to avoid parsing unused fields, and remove the unnecessary network overhead by reducing the number of requests. At the same time, it is important to remember that a single query can potentially generate a lot of database operations. Hence, you cannot assume that the response time for a query increases linear with the number of fields in the query.
The GraphQL schema defines a "cost" per field, which you can take advantage of by analyzing your queries, using following options:
- Inspecting the
x-graphql-query-complexityresponse header and its value. - Using GraphiQL's Profiling functionality to measure the impact.
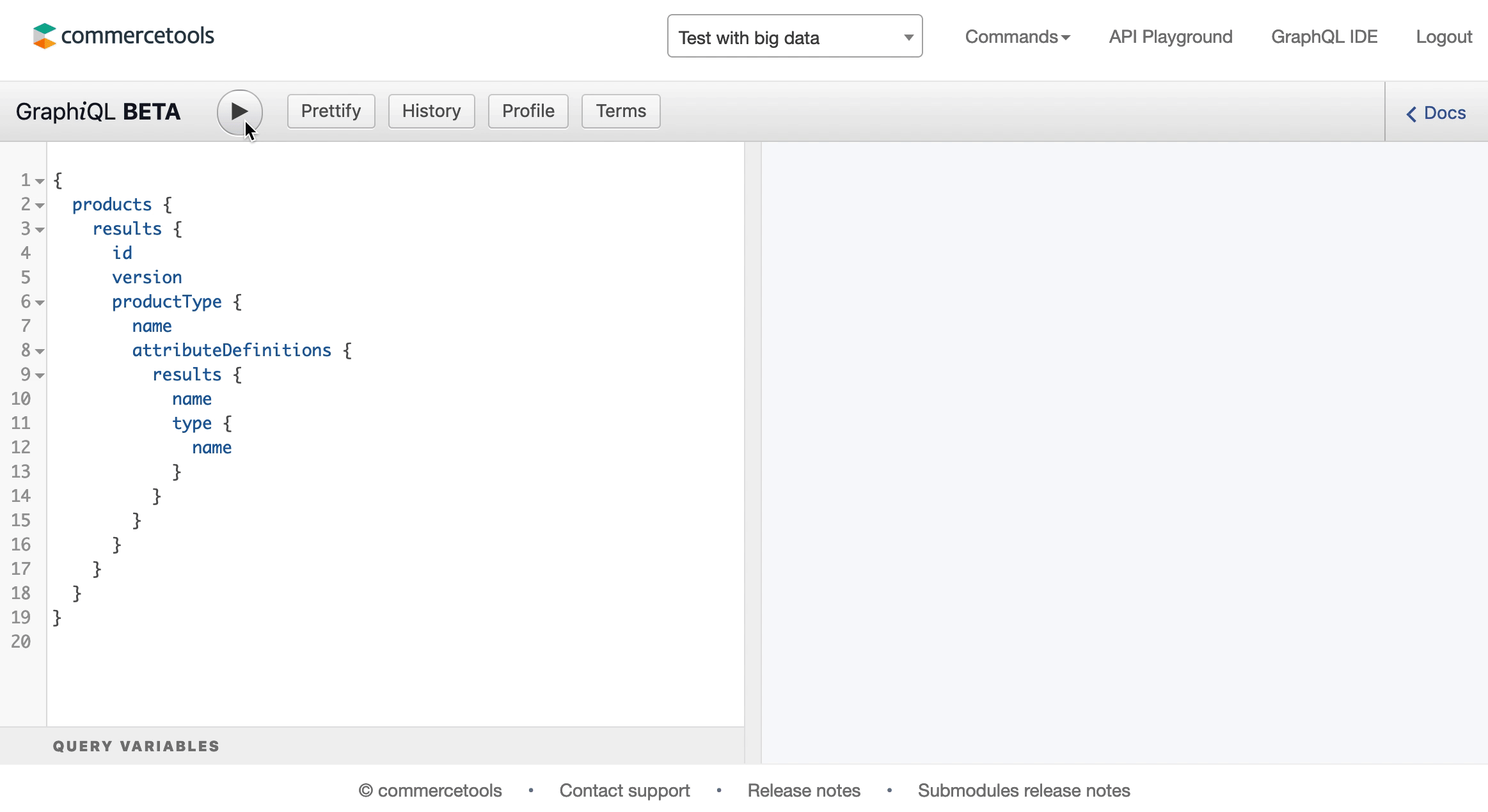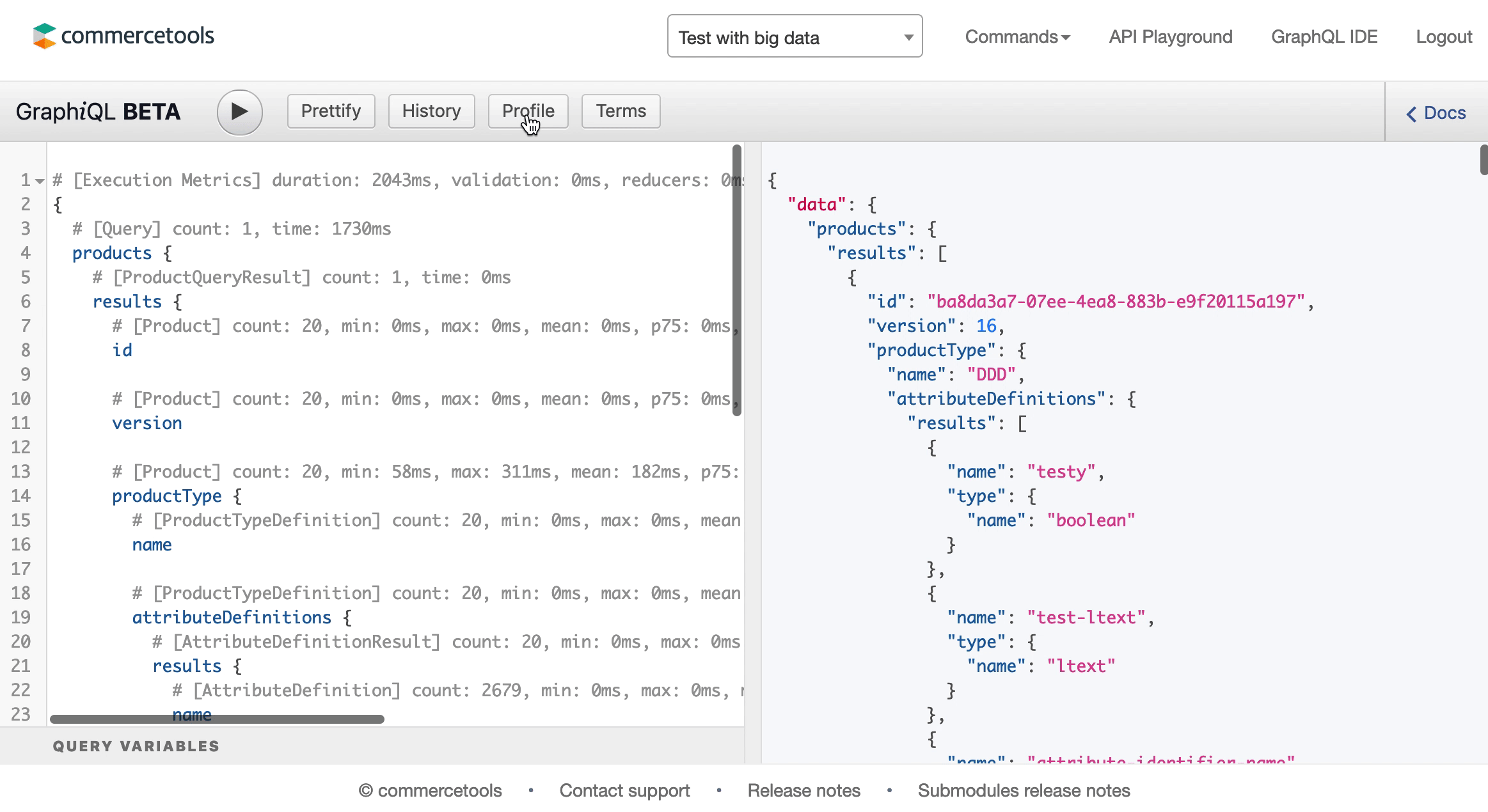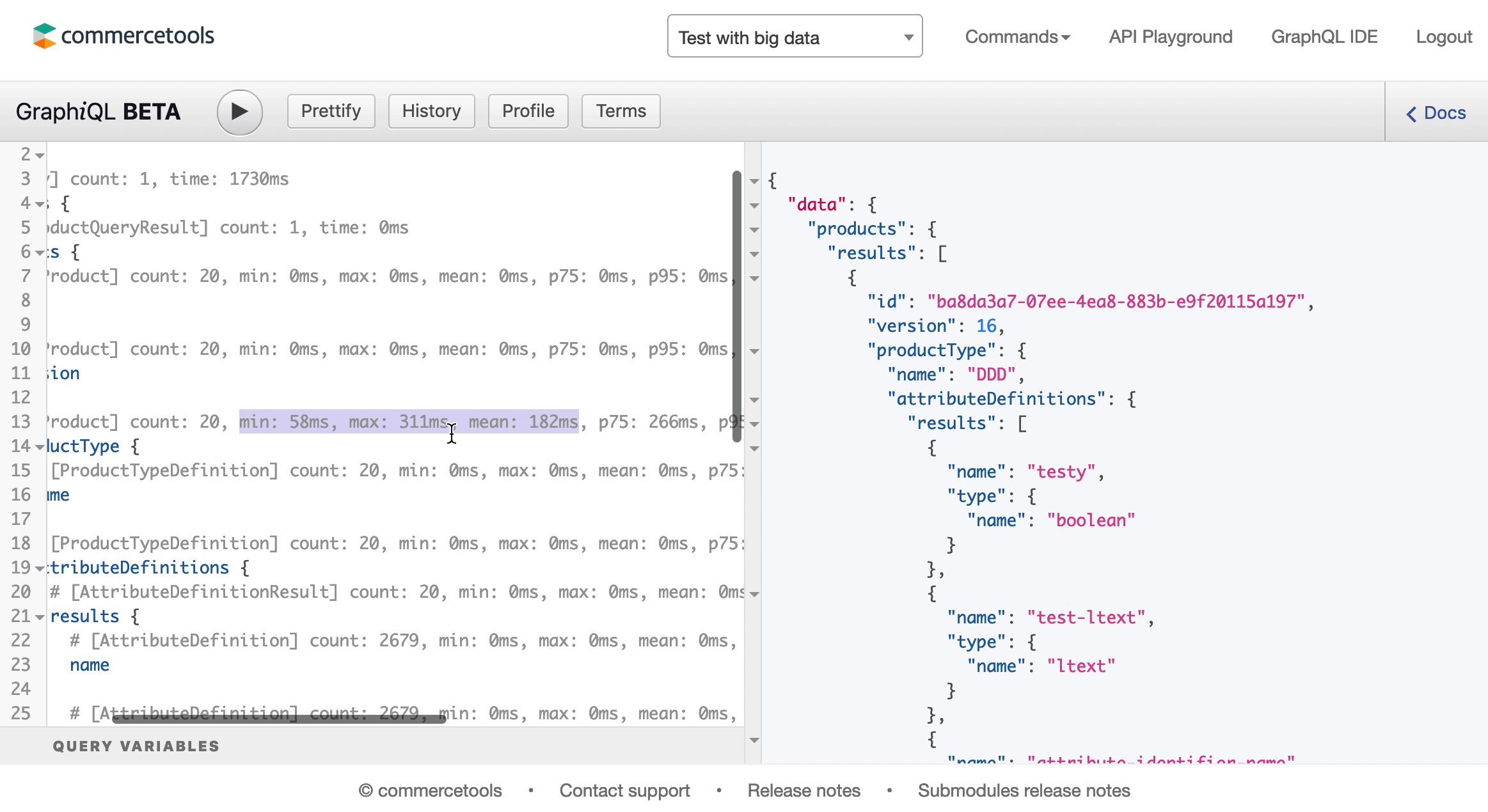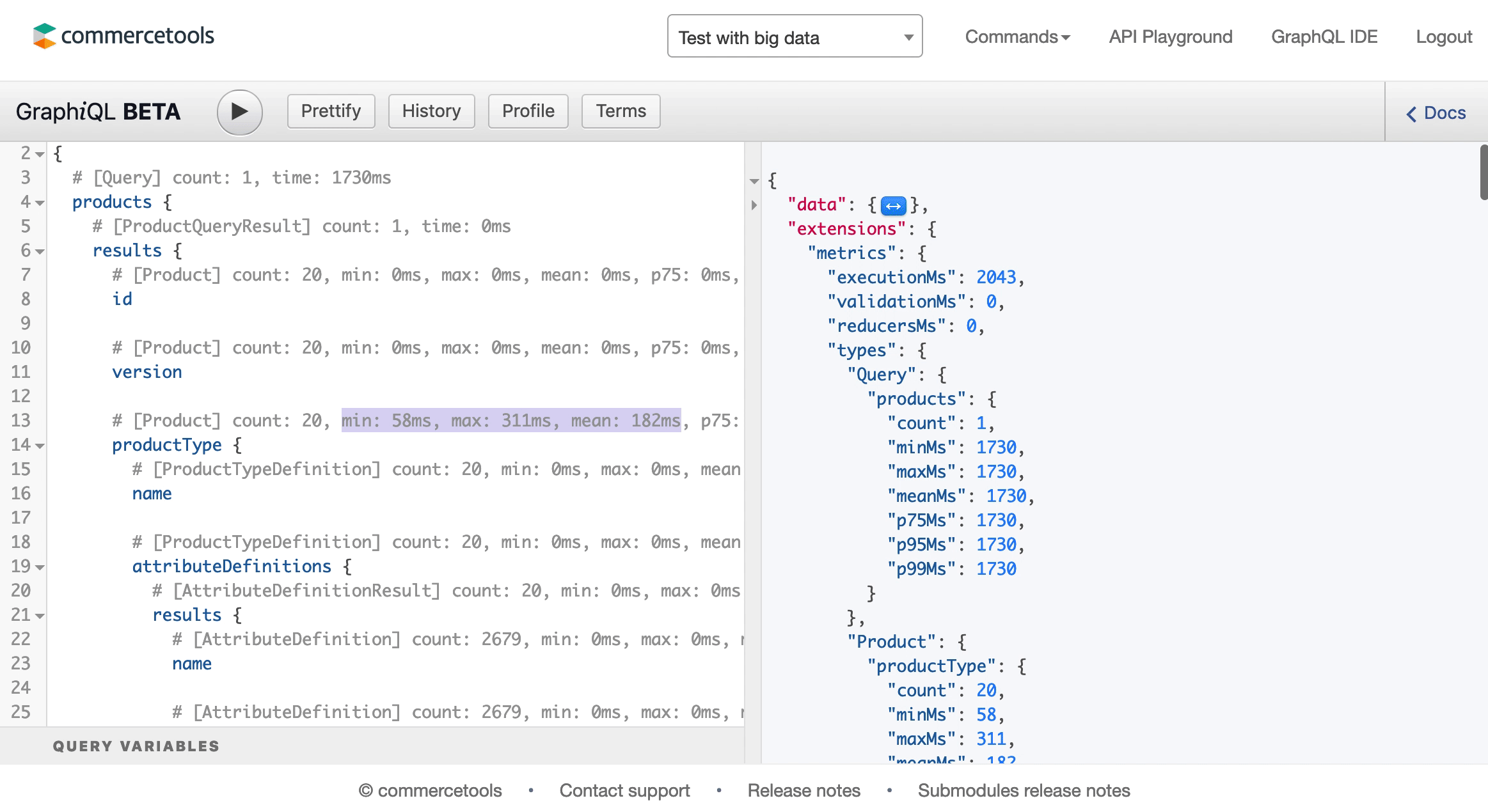
To prevent overly complex queries from having negative impact on the platform, we block queries that exceed the complexity limit of 20 000. If the complexity score for your query is equal or higher than the limit, a QueryComplexityLimitExceeded error code will be returned.
Error response format
The general structure of error responses from the GraphQL API is as follows:
{"errors": [{"message": "Some error message","path": ["somePathSegment"],"extensions": {"code": "SomeErrorCode"}}]}
Each element of the errors array has the following fields:
message- String - detailed description of the error explaining the root cause of the problem and suggesting you how to correct the error.path- Array - Optional - list of query fields ordered from the root of the query response up to the field in which the error occurred. (Only present when an error can be associated to a particular field in the query result).extensions- Object - dictionary with additional information where applicable.code- String - one of the error codes listed on the Errors page.
In the following example we experience a problem on the query path category -> children:
query {category(id:"650fdb2d-93ea-46f9-97f3-a92816b8305e"){children{key}}}
"errors": [{"message": "Too many categories would have been loaded. Please use the 'categories' field instead.","path": ["category", "children"],"extensions": {"code": "InvalidInput"}}]}
Interactive GraphQL console
To explore the GraphQL API, you can use an interactive GraphiQL environment which is available as a part of our ImpEx & API Playground.
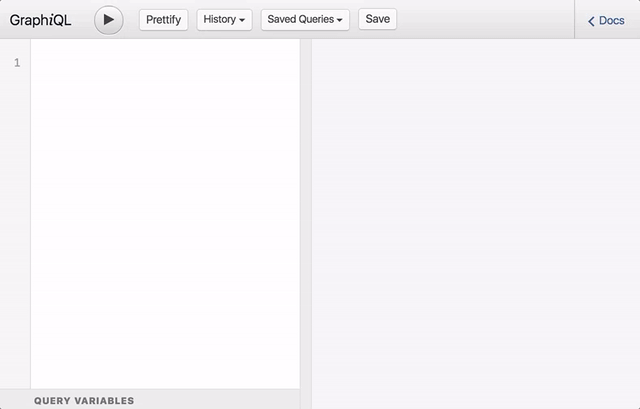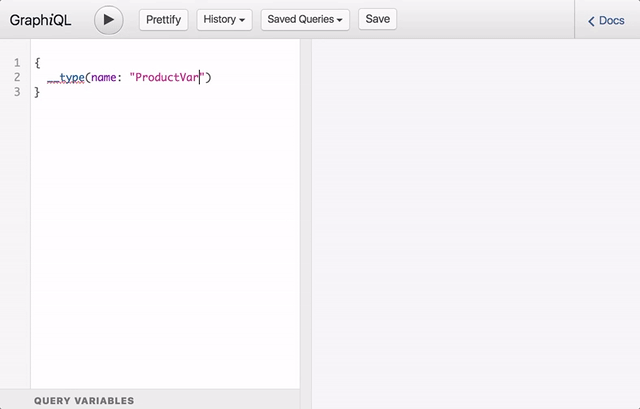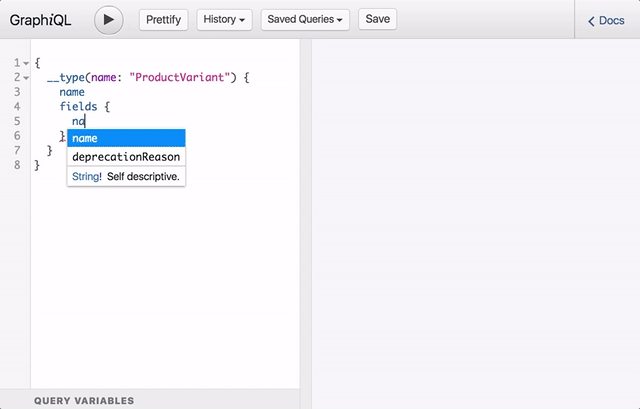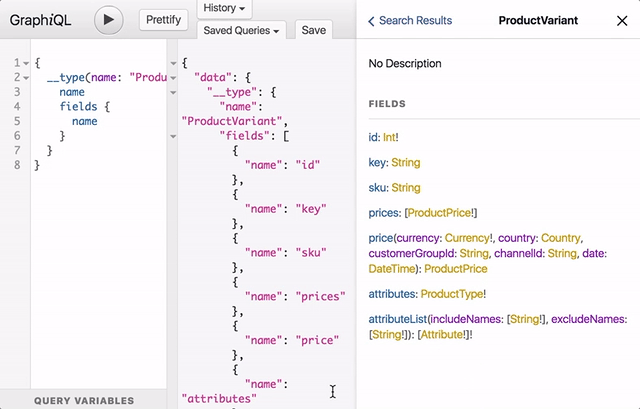
Below animation demonstrates how you can use this tool for autocompletion and to explore the documentation that is part of the GraphQL schema:
Beta functionalities BETA
Find below a list of functionality that is currently in beta.
createdByonVersionedlastModifiedByonVersioned- everything related to
Extension FixedPriceDiscountValueInputonCartDiscountMultiBuyLineItemsTargetandMultiBuyCustomLineItemsTargetonCartDiscount- everything related to
MyCart,MyOrder,MyPayment,MyProfile,MyShoppingList Order EditsonOrderNestedTypesonProductTypeSubrateonTaxCategoryexist